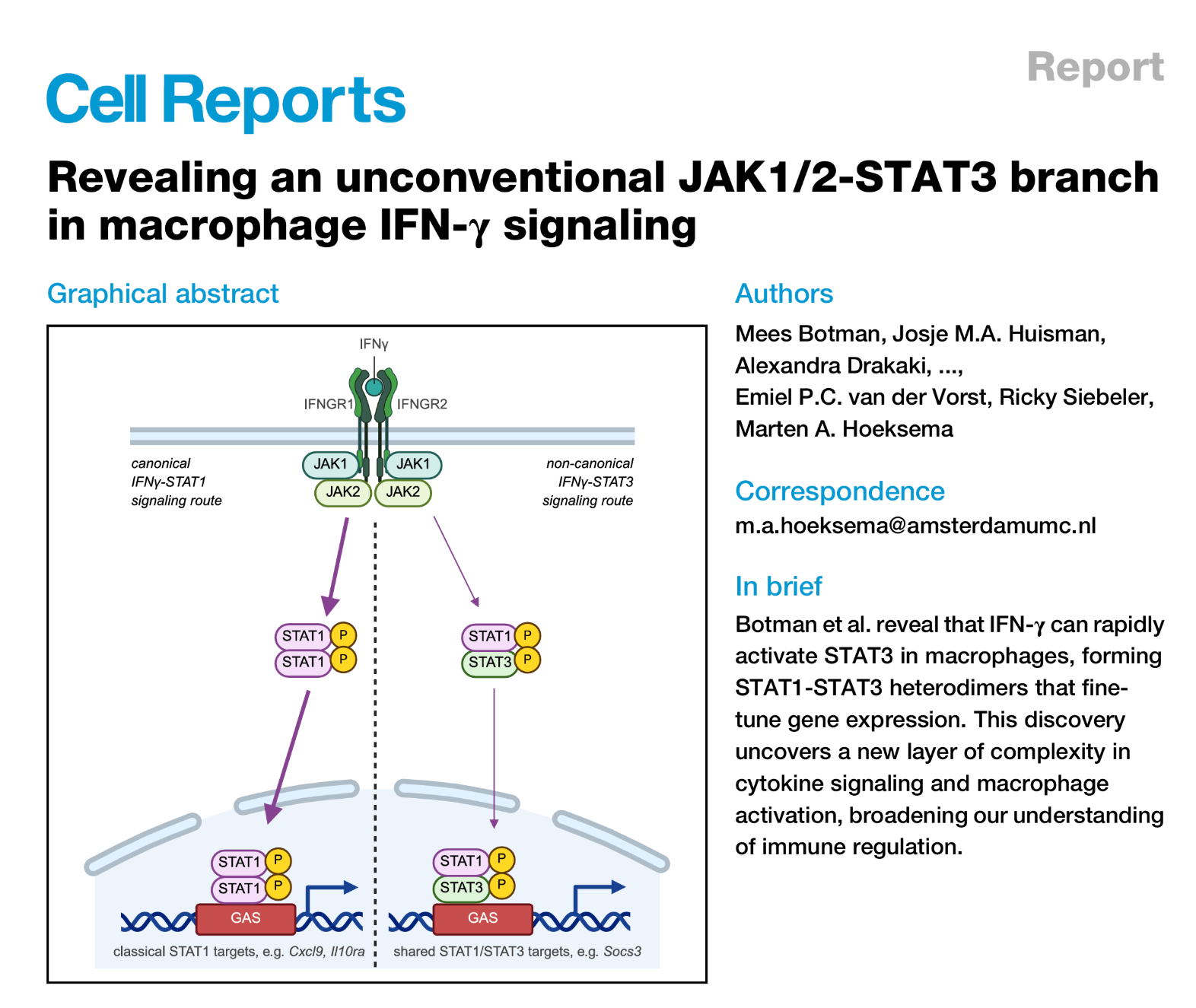
We have a project available for an enthusiastic MSc student!
We study the role of monocytes and macrophages in atherosclerosis, ranging from cardiovascular clinical trials to fundamental research on the epigenetic control of macrophages. The currently available fundamental research project aims to investigate how the Polycomb Repressive Complex 2, which acts on the repressive H3K27Me3 modification, regulates macrophage activation.
Objectives:
I) Generation of CRISPR-Cas9 knock-out cell lines
II) Functional assessment of the effect of the knock-outs on macrophage characteristics.
You will generate knock-out cell lines by cloning, sequencing, genome editing, transduction, transfection, cell culture, and flow cytometry-assisted cell sorting. Once the knock-out cell lines are obtained, various techniques will be at your disposal to functionally assess the knock-out effect on macrophage characteristics, including but not limited to RT-qPCR, ELISA, flow cytometry, and Western blot.
As part of our group, you will join departmental seminars, journal clubs, weekly work meetings, group discussions, and regular social events.
If you would like to acquire molecular biology skills during a 5+ months internship or want more information, please contact r.w.m.kempkes@amsterdamumc.nl or a.e.neele@amsterdamumc.nl